previous post
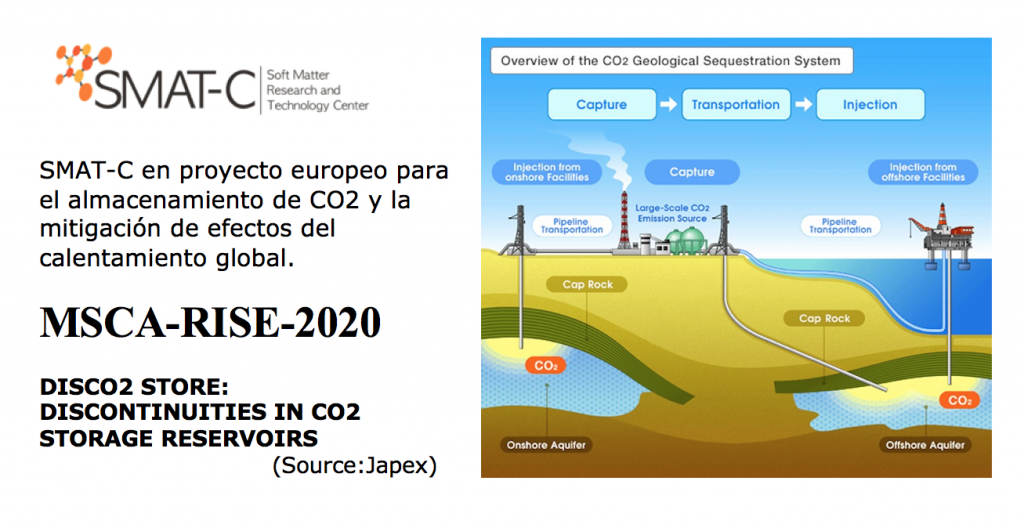
The current scientific consensus indicates that it is vital to reach zero carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by 2050 in order to avoid a large number of negative 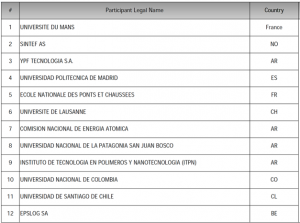 and unprecedented impacts on our planet due to global warming, such as extreme weather events, significant sea level rise, extinction of species and loss of biodiversity, among many others. It is therefore clear that a series of parallel mitigation actions must be undertaken, among which CO2 sequestration in geological repositories plays a major role.A worldwide application of this technology can take place only if a long-term storage of CO2 is assured, which, in turn, depends on a deep understanding of the reservoir characteristics. In this context, naturally-occurring or artificial underground mechanical discontinuities (MDs) are ubiquitous features which constitute the primary reasons for possible hazards associated with CO2 injection operations. DISCO2 STORE consortium thoughtfully examines MDs, in order to provide new knowledge and tools towards a riskless CO2 injection practice.
and unprecedented impacts on our planet due to global warming, such as extreme weather events, significant sea level rise, extinction of species and loss of biodiversity, among many others. It is therefore clear that a series of parallel mitigation actions must be undertaken, among which CO2 sequestration in geological repositories plays a major role.A worldwide application of this technology can take place only if a long-term storage of CO2 is assured, which, in turn, depends on a deep understanding of the reservoir characteristics. In this context, naturally-occurring or artificial underground mechanical discontinuities (MDs) are ubiquitous features which constitute the primary reasons for possible hazards associated with CO2 injection operations. DISCO2 STORE consortium thoughtfully examines MDs, in order to provide new knowledge and tools towards a riskless CO2 injection practice.
Challenges:
This enterprise is tackled by building an interdisciplinary and international network, gathering 12 institutions from EU and TC. It congregates 35 experienced researchers, from academic and non-academic institutions, that share their variety of research expertise by means of international 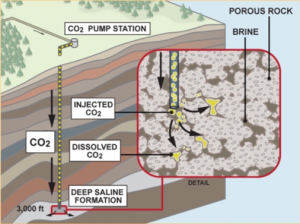 secondments and promote high-level training in a topic of high social impact. In addition, 19 PhD students participate in the project, gaining knowledge and acquiring competences on this environmental hot topic, in an international and stimulating framework. The outputs of this ambitious research proposal permit a deeper understanding of the effects of MDs and contribute towards making CO2 geological sequestration operations a safer and more reachable alternative for the mitigation of the effects of global warming.
secondments and promote high-level training in a topic of high social impact. In addition, 19 PhD students participate in the project, gaining knowledge and acquiring competences on this environmental hot topic, in an international and stimulating framework. The outputs of this ambitious research proposal permit a deeper understanding of the effects of MDs and contribute towards making CO2 geological sequestration operations a safer and more reachable alternative for the mitigation of the effects of global warming.
To know more: francisco.melo@usach.cl